A well-known definition of food insecurity by the United Nations Committee on World Food
Security is, ‘the condition in which all people, at all times, have physical, social and economic access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
What makes Food Security a Sustainable Development Issue?
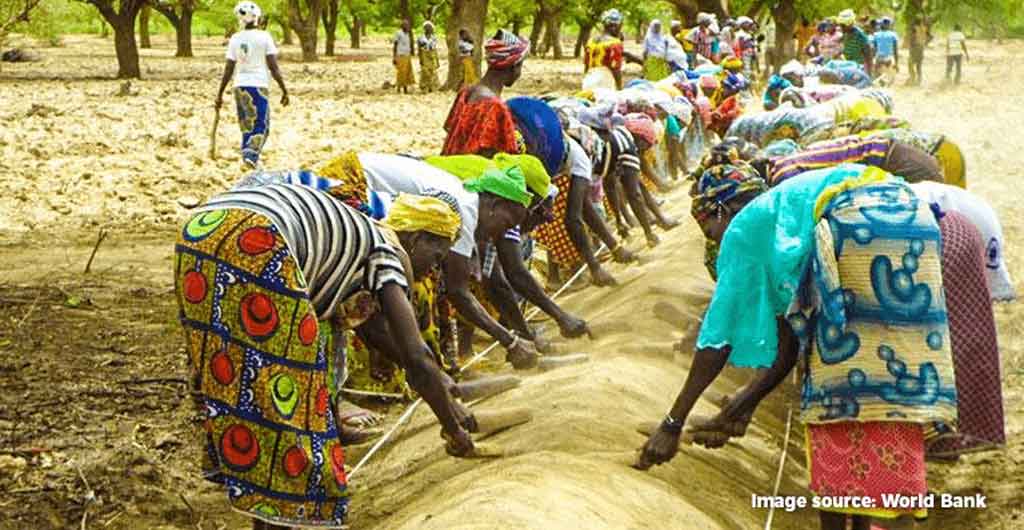
Food insecurity is linked to Social issues such hunger, poverty, inequality and malnutrition. If these issues persist, the achievement of the sustainable development goals which was designed to ‘leave no one behind’ would fall short of full realization. Today, 124 million people globally live in critical levels of food insecurity, requiring urgent humanitarian assistance for their survival. Over half of them live in countries and communities affected by extreme changes in weather patterns, desertification, rising sea levels, floods, conflicts and other humanitarian crisis. With world population projected to grow to 8.5 million by 2030, food insecurity is an urgent challenge to be tackled today. On the global level, efforts are being made to tackle food insecurity through global initiatives like the Famine Action Mechanism launched by the United Nations, the World Bank and other international organisations late last month. The Famine Action Mechanism aims to use data driven technology to predict famine in places around the world and develop adequate strategies to cater for such occurrences. Other organisations such as the World Economic Forum have launched platforms like the Tech Impact 2030 with the aim accelerating the transformation of global food systems through the innovative application of technology.
One of the major causes of food insecurity is food loss.
In a world where 9 out of 10 people are malnourished, it is ironic that a third of all the food produced is lost. In Africa, the value of post-harvest losses in are estimated to equal $4billion per year according to statistics by the African Union. This amount could help feed about 48 million hungry people. In an effort to tackle food loss on the continent the African union set up the continental Post-Harvest Loss Management Strategy with the aim of halving post-harvest loss on the continent by 2025. Back home in Nigeria, several policies have been enacted by the government to support agriculture and hopefully enable food security in the country but food inflation and hunger continue to be pressing issues.
For instance, 2.5 million Nigerian children under the age of five suffer from severe acute malnutrition every year according to a report by the UNICEF. According to the UN, about 240 malnourished children will die daily if urgent actions are not taken especially in the North East. Furthermore, the country has been listed among the 39 countries in need of external assistance by in a recent report by the Food and Agriculture Organisation. Sadly, conflicts in the north eastern part of the country, herdsmen and farmers clashes in the Middle East and climate change have further exacerbated the problem of food insecurity in the country and urgent measures need to be taken to curtail food crises.
If adequate and quality food is to be produced using the proper farm technology this could lead to increased prices of the available food items produced and this definitely excludes a lot of individuals from consuming these food item. This excluded group can without any doubt be classified as the hungry and poor.
The Nigerian Case, how did we get here?
Before the discovery of crude-oil in the 1970’s, produce of the agricultural sector ably sustained the population and economic activities through export. With the growth of other sectors and the influx of industries, more and more people looked to white and blue collar jobs. Agriculture wasn’t prioritized for investment or development, as a result, the sector still lacks 21st century integration of technology and innovation. This also made the sector unattractive as a source of employment to the large youth population. Decades before now, various regions in Nigeria specialised in different kinds of crop productions (food and cash crops).
This system strengthened the country’s food self-sufficiency. For instance, in northern Nigeria, groundnut production was common and the region was known for its groundnut pyramids; western Nigeria was known for cocoa cultivation and had the cocoa mountains, cultivation of palm plantation was common in the eastern Nigeria, the region was known for its oil palm and kernel heaps while the rubber plantation was common in the mid-west.
Besides the systemic neglect of the food and agriculture sector by both the public and private sectors there are other causes for the current trend of food insecurity in Africa’s most populous nation. The country experiences, insufficient food production, climate change, flooding, inadequate technology for processing and storage. There are also the largely spread out social trends of gender inequality, corruption and unimplemented policies.
What Can Be Done?
As with any problem caused by man, it can be solved by man as well. Food insecurity can be addressed through adopting the basic strategies around technology, social, economic and environmental framework.
Already there are inventions, systems and technologies that improve farming efficiency, reduce food waste and improve yields in an effort to tackle the challenge of food insecurity around the world. One of such innovation is the Olio app which is a social food sharing platform aimed at reducing food waste. Another is data driven farming practices that improve a technique known as precision agriculture which aims to increase the efficiency of farmers by accurately predicting the nutrient levels in the soil on farmlands around the world. However, this solution is still very expensive for common farmers but research into the system is still ongoing. Other innovation includes hydroponics and aeroponics systems of farming. After all who says food must be grown on land.
The government can adopt more policies that promotes agricultural biotechnology and mechanized farming in the country, educate farmers on better farming techniques and the use of modern equipment, provide credit facilities, improve present infrastructural facilities and promote the fertilizers and other agro-chemicals.
Further Readings
- Akinyele, I.O. (2009) Ensuring Food and Nutrition Security in Rural Nigeria: An Assessment of the Challenges,
- Ojo, E.O. and Adebayo, P.F. (2012) Food Security in Nigeria: An Overview. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 1, 199-222.
- Saheed Matemilola and Isa Elegbede (2017). The Challenges of Food Security in Nigeria.
- IFPRI – http://www.ifpri.org/topic/food-security
- UNICEF – https://www.unicef.org/nigeria/media_11673.html
- Sustainable Brands https://www.sustainablebrands.com/news_and_views/waste_not/sustainable_brands/african_union_champions_123_unveil_3_latest_weapons_food
- Stears Nigeria – https://www.stearsng.com/article/towards-food-security-in-nigeria